Lesson 4 Network Architecture
Star Topology:
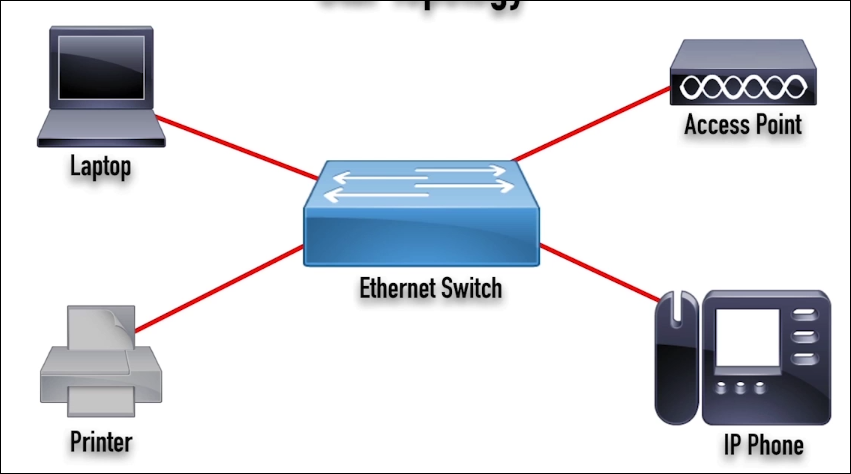
- If one link fails, other links continue to function
- Centralized devices is a potential single point of failure (SPOF)
- Popular in modern networks
Mesh Topology

Number of links needed to support a Full Mesh network supporting all end sites: n*(n01) / 2
example: 5*(5-1)/2 = 10
- Full Mesh Topology
Optimal Path
Not Scalable
More Expensive
- Partial Mesh
Might be Suboptimal Path
More Scalable
- Less Expensive
Hybrid Topology - a network topology that contains elements of multiple topology types
Collapsed Core vs. Three-Tier Architectures
Three-Tier Architectures
- Access
L2 switches
End devices
- Distribution
L3 switches (high capacity, fast)
- Core
Interconnect buildings
Moving packets as quickly as possible between distribution switches
The way out
Ether Channel - a logical interface that is a bundle of multiple physical interfaces, allowing higher throughput between devices, as compared to a single link
Collapsed Core - a two-tier where the Core and Distribution Layers have been consolidated
- Access Layer
Collapsed Core Layer
- Access Layer
- Collapsed Core Layer